Almond
The almond (Prunus dulcis, syn. Prunus
amygdalus Batsch., Amygdalus communis L., Amygdalus
dulcis Mill.), is a species of tree native to the
Middle East and South Asia. Almond is also the name
of the edible and widely cultivated seed of this
tree. Within the genus Prunus, it is classified
with the peach in the subgenus Amygdalus, distinguished
from the other subgenera by the corrugated shell
(endocarp) surrounding the seed.
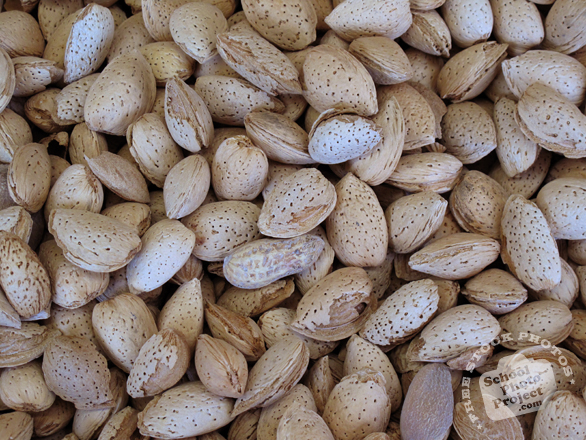
The fruit of the almond is not a true nut, but a
drupe, consisting of an outer hull and a hard shell
with the seed ("nut") inside. Shelling
almonds refers to removing the shell to reveal the
seed. Almonds are commonly sold shelled (i.e., after
the shells are removed), or unshelled (i.e., with
the shells still attached). Blanched almonds are
shelled almonds that have been treated with hot
water to soften the seedcoat, which is then removed
to reveal the white embryo.
The almond is a small deciduous tree, growing 4–10
metres (13–33 ft) in height, with a trunk
of up to 30 centimetres (12 in) in diameter.
The young twigs are green at first, becoming purplish
where exposed to sunlight, then grey in their second
year. The leaves are 3–5 inches long,
with a serrated margin and a 2.5 cm (1 in)
petiole. The flowers are white or pale pink, 3–5
cm (1–2 in) diameter with five petals, produced
singly or in pairs before the leaves in early spring.
Almonds begin bearing an economic crop in the third
year after planting. Trees reach full bearing after
five to six years after planting. The fruit is mature
in the autumn, 7–8 months after flowering.
(Source: Wikipedia.org)
|