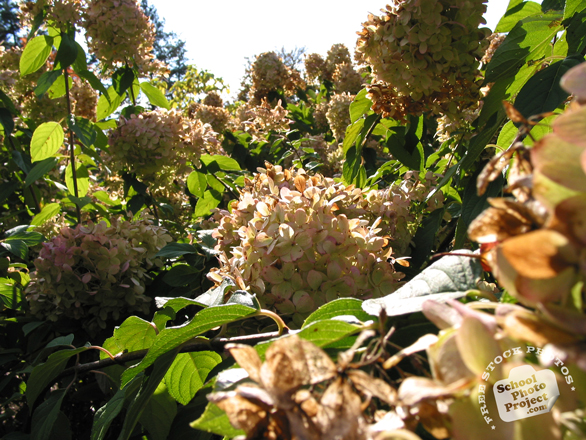
Hydrangea
Hydrangea (common names Hydrangea
and Hortensia) is a genus of about 70 to 75 species
of flowering plants native to southern and eastern
Asia (China, Japan, Korea, the Himalayas, and Indonesia)
and North and South America. By far the greatest
species diversity is in eastern Asia, notably China,
Japan, and Korea. Most are shrubs 1 to 3 meters
tall, but some are small trees, and others lianas
reaching up to 30 metres by climbing up trees. They
can be either deciduous or evergreen, though the
widely cultivated temperate species are all deciduous.
Having been introduced to the Azores Islands of
Portugal, they are now very common there, particularly
on Faial, which is known as the "blue island"
due to the vast number of hydrangeas present on
the island, Terceira, named the "lilac island"
for hydrangeas of that colour, on Flores Island
("Island of Flowers") and Sao Miguel,
named the "green island" for its floral
biodiversity.
Species in the related genus Schizophragma, also
in Hydrangeaceae, are also often known as hydrangeas.
Schizophragma hydrangeoides and Hydrangea petiolaris
are both commonly known as climbing hydrangeas.
There are two flower arrangements in hydrangeas.
Mophead flowers are large round flowerheads resembling
pom-poms or, as the name implies, the head of a
mop. In contrast, lacecap flowers bear round, flat
flowerheads with a center core of subdued, fertile
flowers surrounded by outer rings of showy, sterile
flowers.
(Source: Wikipedia.org)
|