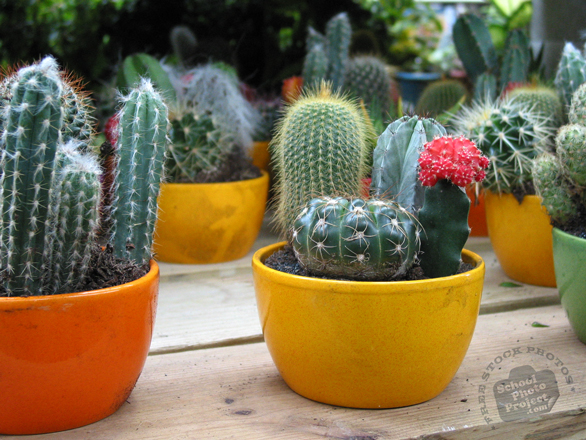
Cactus
A cactus (plural: cacti, cactuses
or cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae.
Their distinctive appearance is a result of adaptations
to conserve water in dry and/or hot environments.
In most species, the stem has evolved to become
photosynthetic and succulent, while the leaves have
evolved into spines. Many species are used for ornamental
plants, and some are also grown for fodder, forage,
fruits, cochineal, and other uses.
Cacti come in a wide range of shapes and sizes.
The tallest is Pachycereus pringlei, with a maximum
recorded height of 19.2 m, and the smallest is Blossfeldia
liliputiana, only about 1 cm in diameter at
maturity. Cactus flowers are large, and like the
spines arise from distinctive features called areoles.
The cactus family is native to the Americas, where
their range extends from Patagonia to southern Canada,
but they are densest and most diverse in the regions
of northern Mexico and the southern tropics of Argentina
and Bolivia. Rhipsalis baccifera is the one exception;
it is native to both the Americas and the Old World,
where it is found in tropical Africa, Madagascar,
and Sri Lanka. It is thought to have colonized the
Old World within the last few thousand years, probably
by being carried as seeds in the digestive tracts
of migratory birds. Many other species have become
naturalized outside the Americas after having been
introduced by people, especially in Australia, Hawaii,
and the Mediterranean region. Cacti inhabit diverse
regions, from coastal plains to high mountain areas.
(Source: Wikipedia.org)
|