Victorian
House
In the United Kingdom, and former
British colonies, a Victorian house generally means
any house built during the reign of Queen Victoria
(1837—1901). During the Industrial Revolution
successive housing booms resulted in the building
of many millions of Victorian houses which are now
a defining feature of most British towns and cities.
In the UK, Victorian houses follow a wide range
of architectural styles. Starting from the early
classicism inherited from Regency architecture,
the Italianate style gained influence in the 1840s
and 1850s, and the Gothic style became prevalent
by the 1880s. Later in the Victorian era, the Queen
Anne style and the Arts and Crafts movement increased
in influence, resulting in the transition to styles
typically seen in Edwardian houses. Victorian houses
are also found in many former British colonies where
the style might be adapted to local building materials
or customs, for example in Sydney, Australia and
Melaka, Malaysia.
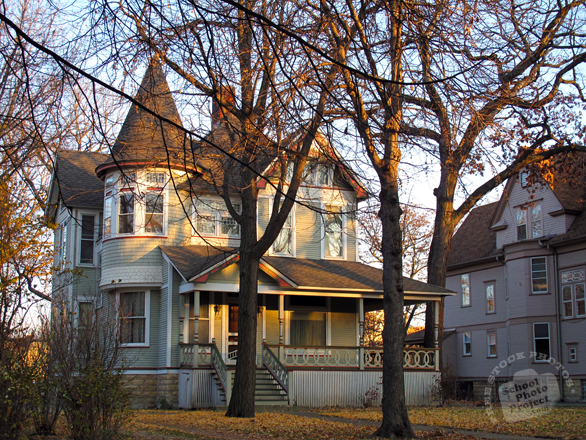
In the United States, Victorian house styles include
Second Empire, Queen Anne, Stick (and Eastlake Stick),
Shingle, Richardsonian Romanesque, and others.
Early in the Victorian era, until the 1840s houses
were still influenced by the classicism of Regency
styles. However the simplicity of Regency classicism
fell out of favour as affluence increased and by
the 1850s the Italianate style influenced domestic
architecture which now incorporated varying quantities
of stucco. From the 1850s domestic buildings also
became increasingly influenced by the gothic revival,
incorporating features such as pointed, projecting
porches, bay windows, and grey slate.
(Source: Wikipedia.org)
|